In the field of construction and civil engineering, the integration of water management and soil testing is critical to ensuring the safety, durability, and environmental sustainability of a project. Two important concepts that intersect in many construction projects are the role of a Water Consultant and the Piling Test. Both play crucial roles in ensuring that the underlying soil and water conditions are well understood and appropriately managed. This article provides an in-depth look at the responsibilities of a Water Consultant and the importance of Piling Tests in construction projects, particularly those involving foundation work.
Understanding the Role of a Water Consultant
A Water Consultant is a specialist who provides advice and services related to the management and mitigation of water-related issues in construction and land development projects. Their primary focus is on managing water resources, ensuring environmental sustainability, and addressing issues that arise due to water, such as flooding, drainage, groundwater management, and water quality.
Key Responsibilities of a Water Consultant
Site Assessment and Water Resource Planning
Water Consultants are often involved early in the planning stages of construction projects, conducting assessments to understand the water-related challenges at a site. This includes studying rainfall patterns, water tables, groundwater flow, stormwater management, and the potential impacts on local ecosystems.
Flood Risk Assessment
For many construction projects, especially those near rivers, lakes, or in flood-prone regions, a Water Consultant conducts flood risk assessments. They analyze historical flood data, soil permeability, and topography to predict potential flooding events and recommend mitigation strategies.
Groundwater Management
Groundwater is a critical factor in many construction projects, especially in areas where water tables are high. A Water Consultant ensures that the extraction, diversion, or management of groundwater does not negatively impact surrounding ecosystems or cause foundation instability.
Stormwater and Drainage Systems
Managing stormwater runoff is another vital responsibility of a Water Consultant. They design and implement drainage systems that prevent flooding and soil erosion while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This may involve designing retention ponds, swales, or incorporating green infrastructure like rain gardens.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Water Consultants also play a critical role in ensuring that a construction project’s water-related activities do not negatively impact the environment. They assess how water usage, treatment, and discharge may affect local rivers, streams, wetlands, or groundwater supplies.
Water Quality Management
In projects that deal with water treatment, such as municipal infrastructure or water supply systems, Water Consultants ensure that water quality is maintained, advising on treatment processes and regulatory compliance.
The Importance of Water Consultants in Construction Projects
Water-related issues can often be overlooked or underestimated, leading to costly delays, structural failures, or environmental damage. A Water Consultant helps mitigate such risks by addressing water management needs and ensuring sustainable practices are employed. Their expertise can save time and money and prevent potential liabilities.
For instance, if a project is situated in an area with a high risk of flooding, the Water Consultant would recommend building techniques such as elevated foundations, flood barriers, or comprehensive drainage systems to protect the site. Similarly, by understanding the water table levels, a Water Consultant might advise on appropriate construction methods, such as deeper foundations or the use of specific materials to prevent water ingress.
What is a Piling Test?
A Piling Test refers to the process of testing piles (long, heavy columns driven deep into the ground) used in the foundation of a structure to assess their load-bearing capacity and the quality of the soil at different depths. Piling is essential when the surface soil is not strong enough to support the weight of a building or structure. The piling test is crucial to ensure that the foundations of a building are stable, safe, and suitable for the loads they will bear over time.
Piling tests are conducted in the field and involve applying various loading methods to determine the response of a pile. These tests are typically performed on different types of piles, including bored piles, driven piles, and screw piles, depending on the project requirements and site conditions.
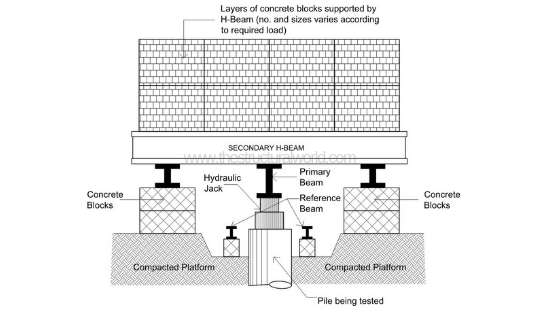
Types of Piling Tests
Static Load Test
The static load test is one of the most common tests performed on piles. During this test, a hydraulic jack is used to apply a load incrementally to the pile. The pile’s settlement (vertical displacement) is measured under each load increment, helping engineers determine whether the pile is capable of supporting the required loads without excessive settlement. Static load tests are useful in confirming the design parameters and ensuring the foundation will perform as expected.
Dynamic Load Test
In dynamic load testing, a pile is subjected to a dynamic force, typically by dropping a heavy weight onto the pile or by striking the pile with a hammer. The resulting vibrations or waveforms are recorded and analyzed to estimate the load-bearing capacity and condition of the pile. The dynamic load test is often faster and less expensive than static load testing, but it provides less detailed information about pile behavior.
Pile Integrity Test (PIT)
The pile integrity test is used to detect defects in the pile or variations in the soil conditions around the pile. In this test, a low-frequency signal is applied to the pile, and the resulting response is analyzed to identify changes in the pile’s condition. This test can detect cracks, voids, or other structural anomalies in the pile, helping engineers to assess the overall integrity of the foundation.
Crosshole Sonic Logging (CSL)
Crosshole Sonic Logging involves sending sound waves through the pile and measuring the time it takes for the waves to travel. This method helps to assess the quality of the concrete within the pile and identify any voids or inconsistencies. CSL testing is highly effective for large-scale projects where pile integrity is crucial for safety.
Pile Driving Analyzer (PDA)
The Pile Driving Analyzer is a system used to measure the forces and displacements during the pile installation process. The data obtained is analyzed to assess the pile’s driving behavior, hammer efficiency, and final capacity. This test provides real-time data and can help optimize the installation process.
The Importance of Piling Tests in Construction
Piling tests are vital to ensuring the safety and stability of a building or structure. Without proper testing, there is a risk that piles may not perform as expected, potentially leading to structural failure or excessive settling. Piling tests allow engineers to evaluate the actual soil conditions and the performance of piles under load, ensuring that the foundation is strong enough to support the planned construction.
For example, the results of a static load test might reveal that a certain type of pile is unsuitable for a given site due to high levels of settlement. With this knowledge, engineers can adjust their designs or choose a different pile type, ensuring that the foundation will be safe and stable throughout the structure's lifespan.
Moreover, testing allows engineers to validate theoretical models and assumptions, which reduces the risks of unexpected outcomes and delays during the construction phase. It also ensures compliance with local regulations, many of which require pile testing for large-scale or critical infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
In modern construction projects, both Water Consultants and Piling Tests are indispensable elements for ensuring the stability, safety, and environmental sustainability of a structure. Water Consultants play a pivotal role in managing water resources, preventing flooding, and ensuring that groundwater issues do not undermine the foundation of a project. Meanwhile, piling tests provide essential data about soil conditions and pile performance, ensuring that the foundation can support the intended loads.
Both practices help to minimize risks and optimize design, ensuring that construction projects are completed on time, within budget, and without compromising on safety or environmental integrity. As the construction industry continues to evolve, these roles and tests will only become more critical in ensuring that infrastructure is resilient, sustainable, and safe for future generations.



