Introduction:
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that involves nerve damage due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels. In this comprehensive overview, we delve into the intricacies of diabetic neuropathy, exploring its types, symptoms, risk factors, and the impact it has on the lives of individuals with diabetes.
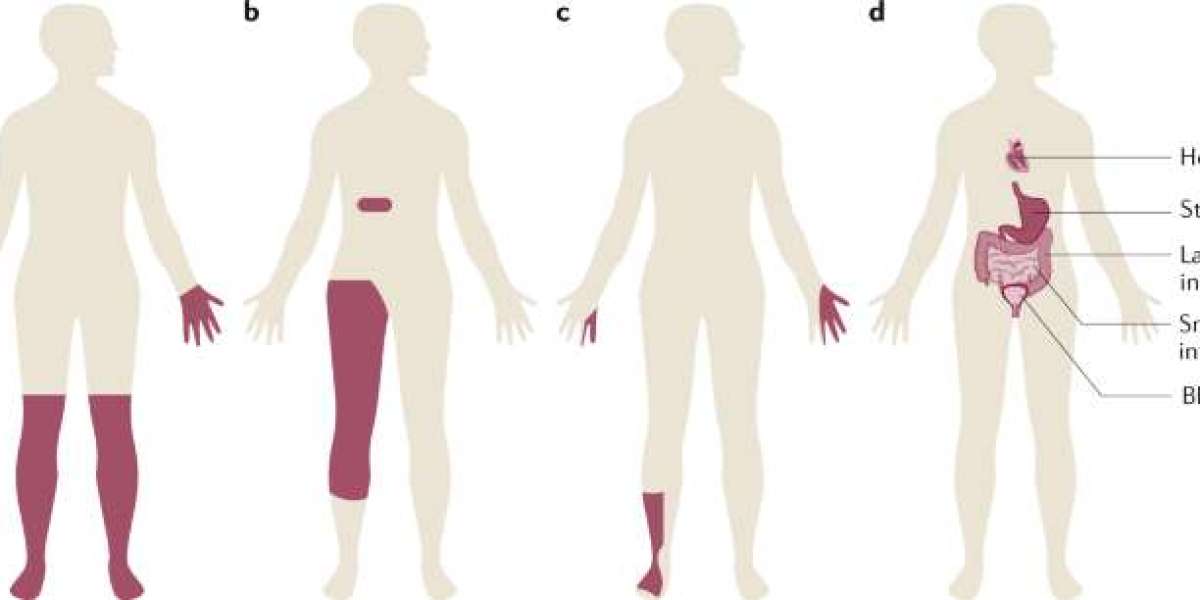
- Types of Diabetic Neuropathy:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: The most prevalent form, peripheral neuropathy affects the peripheral nerves responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. Symptoms may include tingling, numbness, and pain in the extremities.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: This type affects the autonomic nervous system, impacting involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and bladder control. Symptoms may include dizziness, gastrointestinal issues, and difficulty regulating blood pressure.
- Proximal Neuropathy: Also known as diabetic amyotrophy, proximal neuropathy typically affects the hips, thighs, and buttocks. It can cause severe pain, weakness, and muscle wasting.
- Focal Neuropathy: Focal neuropathy results in the sudden onset of neurological deficits in specific nerves. It often causes pain and weakness in the affected area, such as the hand, head, or torso.
- Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy:
- Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms: Individuals with peripheral neuropathy may experience tingling, burning sensations, or pain in the hands and feet. Numbness, sensitivity to touch, and muscle weakness can also occur.
- Autonomic Neuropathy Symptoms: Symptoms may manifest as digestive issues, such as gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying), cardiovascular problems, including changes in heart rate, and urogenital symptoms such as sexual dysfunction and incontinence.
- Proximal Neuropathy Symptoms: This type may cause severe pain in the hip or thigh, leading to difficulty standing from a seated position or walking. Muscle weakness and atrophy can also occur.
- Focal Neuropathy Symptoms: Symptoms depend on the affected nerve and may include sudden pain, weakness, or paralysis in specific areas. For example, focal neuropathy affecting the eyes may cause double vision.
- Risk Factors and Prevention:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial in preventing and managing diabetic neuropathy. Regular monitoring, adherence to medication regimens, and lifestyle modifications contribute to stable blood glucose levels.
- Blood Pressure Management: Hypertension can exacerbate diabetic neuropathy. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and prescribed medications is essential for preventing further nerve damage.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management can have a positive impact on preventing and managing diabetic neuropathy.
- Regular Checkups: Routine medical checkups, including comprehensive foot exams, eye examinations, and neurological assessments, are vital for early detection and intervention.
- Diagnostic Approaches:
- Clinical Assessment: Healthcare providers conduct a thorough clinical assessment, considering a patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings.
- Neurological Examinations: Neurological exams, including sensory and motor function tests, help identify signs of nerve damage. Reflexes, coordination, and muscle strength are evaluated.
- Electrodiagnostic Tests: Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) can assess the extent of nerve damage and identify specific nerves affected.
- Imaging Studies: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans may be used to rule out other potential causes of symptoms and identify structural abnormalities.
- Management and Treatment:
- Medications: Various medications like pregabalin 75 mg prescribed to manage symptoms and slow the progression of diabetic neuropathy. These may include pain relievers, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants.
- Blood Sugar Control: Tight glycemic control is a cornerstone of diabetic neuropathy management. This involves optimizing insulin or oral medication regimens and making dietary and lifestyle modifications.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing diabetic neuropathy. Tailored exercise programs can improve strength, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing overall mobility.
- Pain Management Techniques: Pain management strategies may include the use of topical treatments, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and other non-pharmacological approaches to alleviate discomfort.
- Foot Care: Proper foot care is essential to prevent complications such as foot ulcers and infections. Regular foot inspections, appropriate footwear, and routine podiatric care are integral components of diabetic neuropathy management.
Conclusion:
Diabetic neuropathy is a multifaceted complication of diabetes that demands a comprehensive approach to understanding, prevention, and management. Through early detection, optimal blood sugar control, lifestyle modifications, and targeted treatments, individuals with diabetes can mitigate the impact of neuropathy on their quality of life. With ongoing research and advancements in diabetic care, the medical community continues to refine strategies for preventing, diagnosing, and effectively managing diabetic neuropathy.